The Allee Effect Is Used to Describe a Population That
The strong Allee effect is a population that satisfies dx rc dt G - 1 1 - i - A where 0 A K. E carrying capacity is never reached.

Allee Effects In Biological Invasions Taylor 2005 Ecology Letters Wiley Online Library
39 The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.

. In this paper we develop a population equation based on the Ricker model with periodic carrying capacity and embedded mechanisms of both weak and strong types of Allee effect. There was also no demographic Allee effect in the HiP wild dog population as the population growth rate was significantly negatively related to population size. C only density-dependent factors affect the rate of population growth.
The per capita rate of population increase r measures species fitness. The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. D only density-independent factors affect the rate of population growth.
A potentially important. B Sketch the general solution for xt. The terms weak and strong Allee effects are in my experience used in a couple of different ways.
28 The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. The first part of the chapter describes the progression of the ideas in ecology that led a mostly competition oriented view of both behavioural ecology and. First Allee effects also positive density dependence can be modelled in several different ways and the equation you give is one example.
HiP South Africa to describe population and pack dynamics. E is in crash decline. It explains what an Allee effect is provides a clear definition of the main concept and of its nuances and briefly explains how it works both at the individual and population levels.
C approaches carrying capacity. It is sometimes referred to as undercrowding and it is analogous or even considered synonymous by some to depensation in the field of fishery sciences. E carrying capacity is never reached.
B has become so large it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. D exceeds carrying capacity. B has become so large that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
We used this extensive data set to test the prediction that if Allee effects occur aspects of repro-. C is viable and stable at its carrying capacity. An Allee effect or depensation is a situation at low population densities where the per-individual growth rate is an increasing function of population density.
D has exceeded its carrying capacity. In population ecology the logistic theta-logistic and the Allee effect models are used to describe the growth of populations under different responses to biotic stress induced by population density. In population ecology the logistic theta-logistic and the Allee effect models are used to describe the growth of populations under different responses to biotic stress induced by population density.
C only density-dependent factors affect the rate of population growth. B has become so large it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. When it is used as endpoint the responses to population density seem.
Most often strong density dependence is used to denote Allee effects where the per capita population growth. B has become so large it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. This paper develops mathematical models to describe the growth critical density and extinction probability in sparse populations experiencing Allee effects.
The generally accepted definition of Allee effect is positive density dependence or the positive correlation between population density and individual fitness. What happens when x0 A. C Describe a specific population that might be affected in this way and be specific about why.
A Sketch the function on the right-hand side of the ODE above. 39 The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. D only density-independent factors affect the rate of population growth.
In population ecology the logistic theta-logistic and the Allee effect models are used to describe the growth of populations under different responses to biotic stress induced by population density. A reaction-diffusion-advection equation with strong Allee effect growth rate is proposed to model a single species stream population in a unidirectional flow. Here random undirected movement of individuals in the environment is described by passive diffusion and an advective term is used to describe the directed movement in a river caused by.
An innovation in this context is to make the intensity explicitly dependent on a parameter q appearing as a. When it is used as endpoint the responses to population density seem to perfectly correspond to LNT Threshold and Hormetic responses to. E is in crash decline.
C approaches carrying capacity. Up to 10 cash back The Allee effect describes populations that deviate from logistic growth models and arises in applications including ecology and cell biology. E is in crash decline.
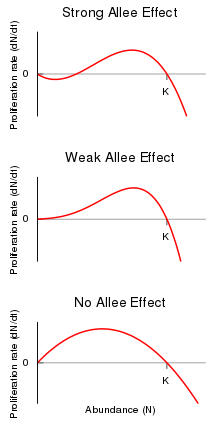
The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing. The null hypothesis is when the proliferation rates are decreasing at low. Has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
Up to 10 cash back The adjective attenuated is used to describe different degrees of intensity that weak or strong Allee effects may have. Allee effect is categorized by the essence of dependence on density which is relatively lower. Allee effects are one of the classic phenomena of population ecology.
A region is claimed to possess a robust Allee effect when the population shrinks to lower densities and a weak Allee effect when the proliferation rate is high and positive. C approaches carrying capacity. The existence of a threshold size for the viability of populations subject to a strong Allee effect gives rise to a wide range of consequences for the establishment and extinction of biological populations the speed of spread and the expected persistence over long times.
39 The Allee effect is used to describe a population that A 30. The per capita rate of population increase r measures species fitness. A potentially important mechanism.
A common justification for incorporating Allee effects into population models is that the population in question has altered growth mechanisms at some critical density often referred to as a. Listed below are a few significant subcategories of the Allee effect. D exceeds carrying capacity.
An Allee effect or depensation is a situation at low population densities where the per-individual growth rate is an increasing function of population density.

Depensation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

A Logistic B Weak Allee Effect C Strong Allee Effect The Graphs On Download Scientific Diagram

Definitions Of Various Allee Effects Note Function F P Is Per Capita Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "The Allee Effect Is Used to Describe a Population That"
Post a Comment